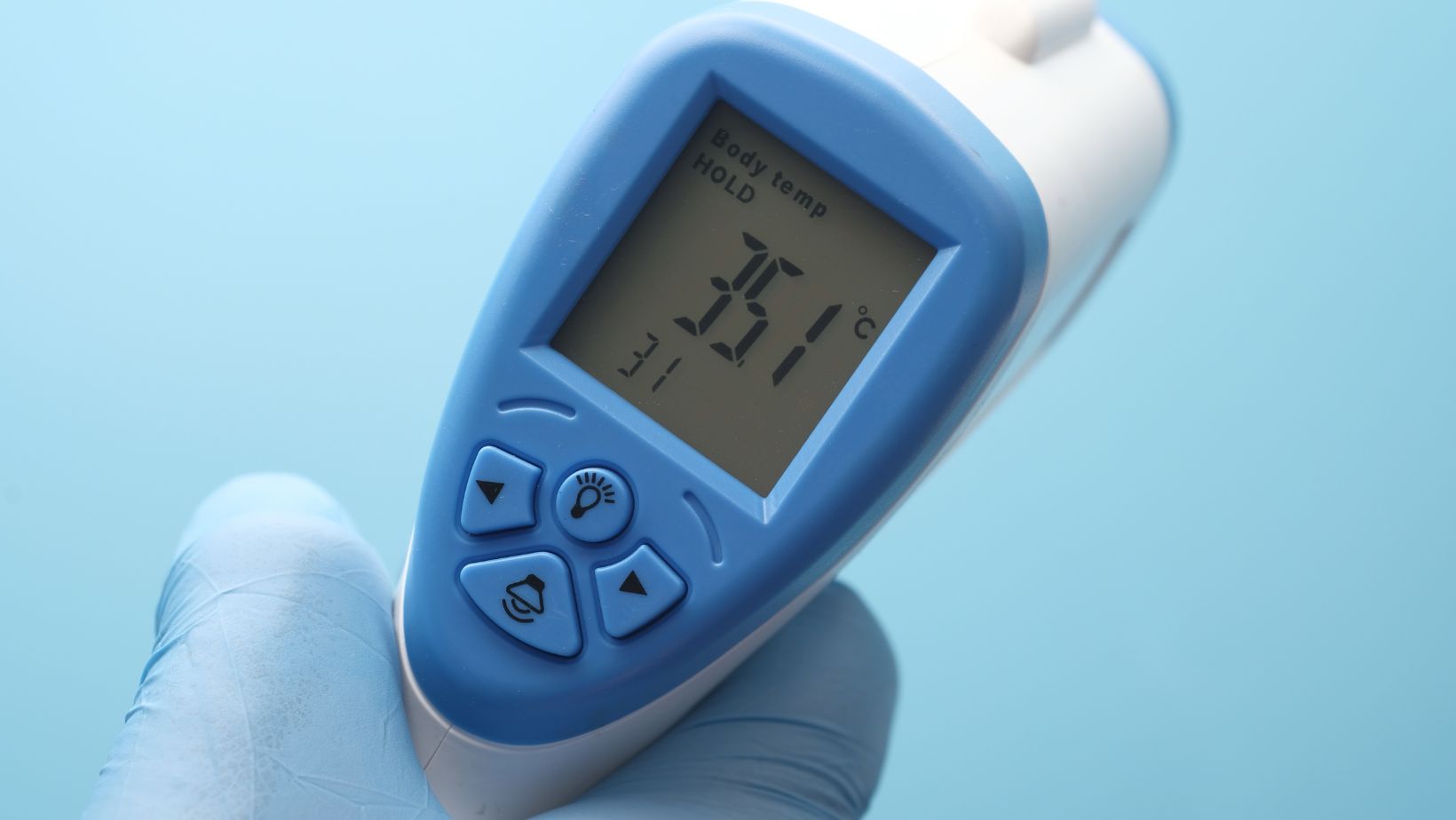
In the current health, and efficiency-oriented landscape temperature thermometers have gone past the rudimentary mercury-based ones, long before them was present in various households in the medicine cabinet. Available in all forms of digital readers to industrial-level infrared devices, temperature thermometers play a vital role in ensuring that both safety, quality, or wellness are adherent in different environments.
A quick example of appropriate thermometer use could be used to measure the temperature of a child with fever, food in commercial kitchen, and a motor in an industrial facility since accurate measurements are achieved to make decisions. This guide discusses the various temperature thermometers that are in existence, their uses and selecting the best one.
What are Temperature Thermometers?
In essence, temperature thermometers are devices that are utilized in the measurement of heat or thermos-energy. They register much more value than we can imagine, and these are enabling us to find out the presence of an illness, quality of a product and performance of a mechanical system.
There are varieties of thermometers in the modern world:
- Healthcare digital oral, ear rectal thermometers
- Non-contact thermometers such as the infrared thermometers
- Scientific and industrial thermocouple products
- Oven thermometers and HVAC Systems: thermometers based on a bimetallic strip
Not all of them can be used interchangeably as they have different purposes and knowing the difference is the most important when buying one.
Temperature Thermometers Applications
1. Medical Use
Digital thermometers are still common in both the hospitals and homes. They offer fast and precise readings and are very useful in detecting the fevers in adults and children. Ear and forehead models are particularly convenient to young children.
2. Food Safety
Temperature control is necessary in the work of commercial kitchens and restaurants. Thermometers in food keep the meat safe and cold foods to remain at the about required temperature to avert growth of bacterial infections.
3. Lab and Factory conditions
The temperature thermometers applied to laboratories and plants require dealing with extreme variations and providing maximum accuracy. They are normally used to manufacture thermocouples and resistance temperature detector (RTDs) due to reliability and durability.
4. Domestic use and HVAC/Air Conditioning Use
Thermometers can be either used to check the room temperature, or used to track the health of home appliances, and are, therefore, effective in day-to-day convenience and energy-efficiency. To check on the systems, HVAC professionals are equipped with specific thermometers that help them know whether their systems are working properly or not.
The Greatest Way to Choose a Temperature Thermometer.
In choosing a thermometer, you should bear in mind:
- Precision: Seek models that are precise, particularly when they will be used in medicine and science.
- Response Time: Rapid readings enhance convenience, particularly in an environment where fast children or people are.
- Usage: Depending on your need, you can make use of a thermometer used in medicine, food, industry, or personal recording.
- Ease of Use: Backlit displays, the ability to store memory, and easy interfaces, are some components that make thermometers easier to use.
- Safety: To use in medicine, make sure that the thermometer was safe to use by all ages and can be easy to wash or sterilize.
Final Thoughts
The thermometers used to measure temperature are nowadays a common necessity in almost every industry and family. Now plenty of varieties are available in the market, using which not only accuracy and safety but also peace of mind can be improved. If you are about to have a dependable helper in your kitchen you will find a thermometer to be your companion. Similarly, as it is in the service of your health and possibly your rise and fall in business.
A good temperature thermometer will always keep you one step before the rest- be it health monitoring, safety monitoring or performance monitoring.